反射概念
反射指的是通过一个类就能知道该类的所有属性和方法(注意这里是类,而不是实例化的对象)。通俗的说,就是给你一个类的名称就可以得到该类的成员变量、构造方法、成员方法的技术。
通过类得到其所有的属性和方法。举个例子,比如有汽车这个类,通过汽车我们能够知道他的组成部分有轮子、方向盘等。将轮子、方向盘视为一个对象,然后通过该对象可以进行一些操作,比如轮子本身具有向前的功能,方向盘具有转弯的功能。这就是反射(内省)机制的形象化理解。
那么问题来了,到底哪里体现了反射的字面意思呢?文末有讲到,建议按照顺序读完。
字节码对象(Class对象)-标识.class文件的对象
反射机制中有两个对象的概念对理解反射非常重要,下面介绍字节码对象
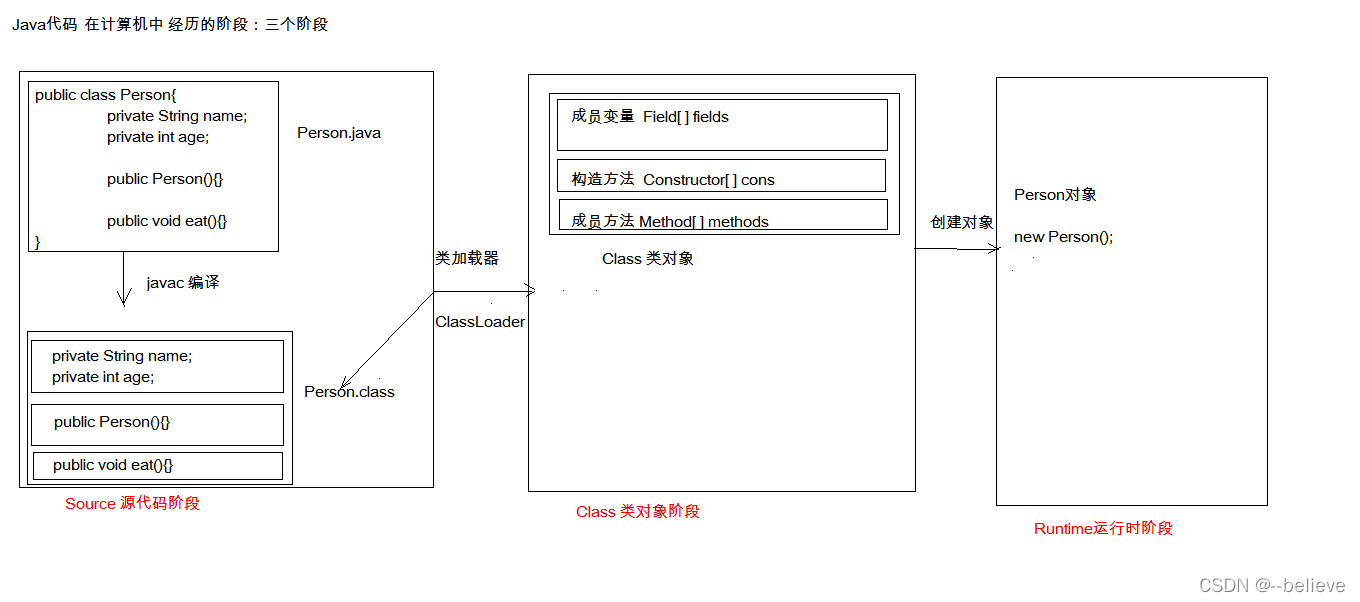
我们知道一个java文件,需要编译成.class文件。这个.class文件我们虽然表面上对该文件一无所知,但是java将.class字节码加载进内存时,jvm将产生一个java.lang.Class对象代表该.class字节码文件(这里体现了java中万物皆对象),从该字节码文件中可以获得该类的许多基本信息,这就是反射机制。所以要想完成反射操作,必须先获得该字节码对象。下面介绍三种获取字节码对象方法。
获取Class对象的三种方法
Class.forName(“全类名”)
1
| Class.forName("cn.itcast.reflect.domain.Student");
|
如果知道一个类的全类名,就可以通过该方法来得到类对象。这里的Class是java系统中自己定义的类。
自定义类名.class
通过自定义类名的属性来获取。
对象.getClass
通过实例化的对象,get方法来获取
字节码对象功能(获取类属性和方法对象)
上面我们介绍了获取字节码对象三种方法后,再来介绍该对象的功能。
我们说过,字节码对象代表.class文件,可以通过该字节码对象了解到.class字节码编译前java类中的所有属性和方法。下面介绍这些属性和方法封装成的对象:Filed、Constructor、Method如何获取。
获取成员变量们
- Field[] getFields() :获取所有public修饰的成员变量
- Field getField(String name) 获取指定名称的 public修饰的成员变量
- Field[] getDeclaredFields() 获取所有的成员变量,不考虑修饰符
- Field getDeclaredField(String name)
获取构造方法们
- Constructor<?>[] getConstructors()
- Constructor getConstructor(类<?>… parameterTypes)
- Constructor getDeclaredConstructor(类<?>… parameterTypes)
- Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors()
获取成员方法们
Method[] getMethods()
Method getMethod(String name, 类<?>… parameterTypes)
Method[] getDeclaredMethods()
Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, 类<?>… parameterTypes)
到底哪里体现反射的字面意思?
一图胜千言,看图
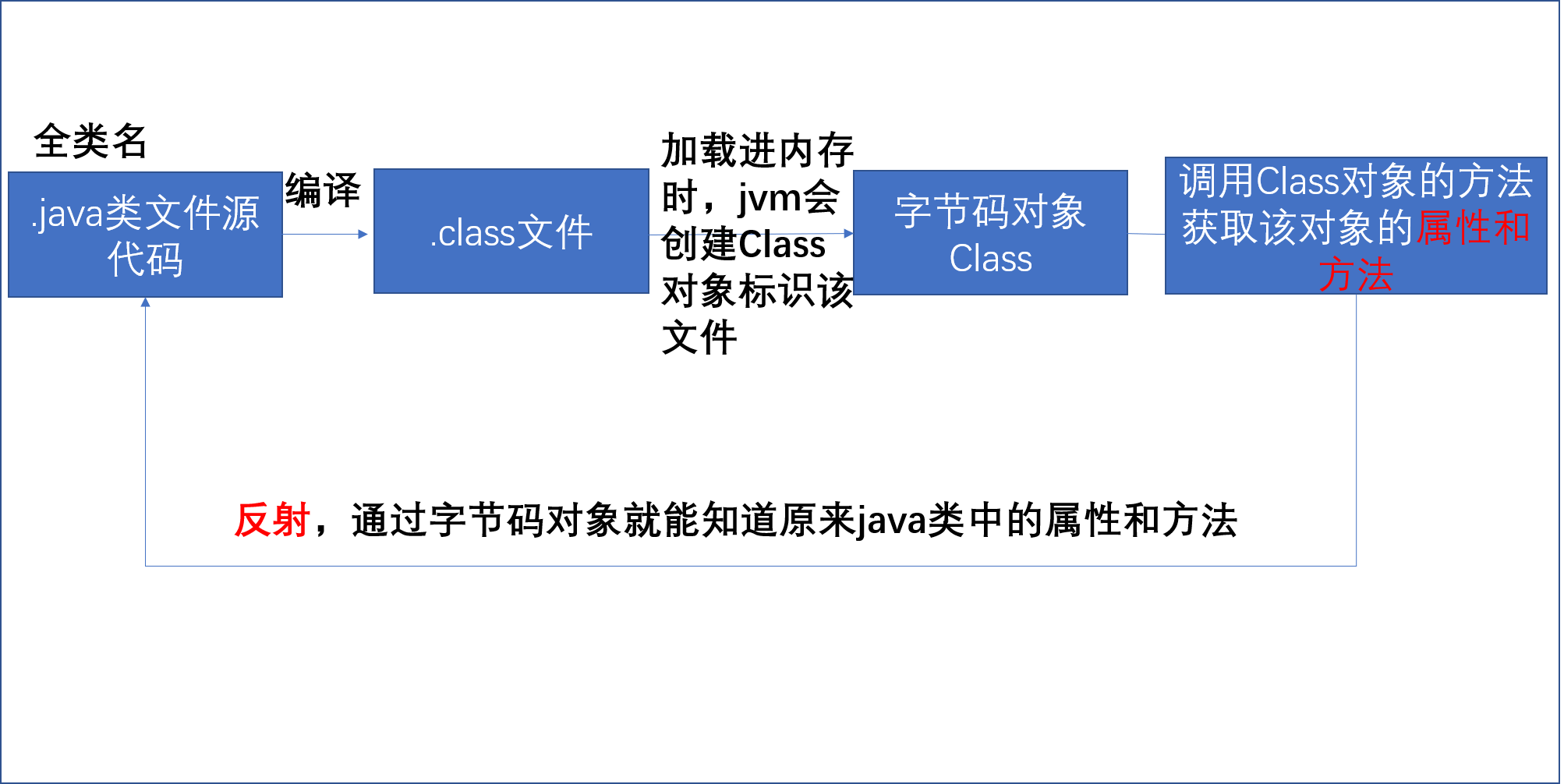
反射体现在通过字节码对象,反射回推得知java类中所有的属性和方法。
其实探究反射到底体现在哪里,这里不是太重要?重要的是需要理解反射指的是通过类了解到该类内部的属性和方法的一种技术。
案例:实现小框架理解反射是框架的灵魂
需求:通过加载properties,实现调用任意一个类的方法。(不允许使用new实例对象的方法来调用函数。)
方法:
1.加载property对象
1
2
3
| Properties pro = new Properties();
InputStream resourceAsStream ==example.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("pro.properties");
pro.load(resourceAsStream);
|
2.通过property对象读取属性全类名,创建字节码对象
1
2
| String className = pro.getProperty("className");
Class cls = Class.forName(className);
|
3.通过字节码对象获取并实例化类构造对象
1
2
| Constructor constructor = cls.getConstructor();
Object o = constructor.newInstance();
|
4.通过字节码对象获取并执行类方法对象
1
2
| String methodName = pro.getProperty("methodName");
cls.getMethod(methodName).invoke(o);
|
example.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| package cn.itcast.reflect;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.Properties;
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Properties pro = new Properties();
InputStream resourceAsStream = example.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("pro.properties");
pro.load(resourceAsStream);
String className = pro.getProperty("className");
Class cls = Class.forName(className);
Constructor constructor = cls.getConstructor();
Object o = constructor.newInstance();
String methodName = pro.getProperty("methodName");
Object invoke = cls.getMethod(methodName).invoke(o);
}
}
|
pro.properties
1
2
| className=cn.itcast.domain.Student
methodName=shout
|
Person.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| package cn.itcast.domain;
public class Person {
public String name;
public Integer age;
private String address;
public Person() {
}
public void shout(){
System.out.println("我是person......");
}
public Person(String name, Integer age, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
|
Student.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| package cn.itcast.domain;
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String address;
public void shout(){
System.out.println("我是student.......");
}
public Student() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Student(String name, Integer age, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
|
文件目录结构