协议设计与解析
为什么需要协议
TCP/IP消息传输是基于二进制流的方式,没有边界。
协议的目的就是划定消息的边界,制定通信双方要共同遵守的通信规则。
例如:在网络上传输
是中文中一句著名的无标点符号的句子,没有标点符号,有很多种拆解方式,不同拆解有不同的意思。这就是说明了标点符号的重要性,也就是消息边界的重要性。
网络中的协议,也就是给网络传输的信息加上「标点符号」。下面一种协议较为常用
netty中通过LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder来实现。
redis协议举例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
byte[] LINE = {13, 10};
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(worker);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
set(ctx);
get(ctx);
}
private void get(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer();
buf.writeBytes("*2".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("$3".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("get".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("$3".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("aaa".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf);
}
private void set(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer();
buf.writeBytes("*3".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("$3".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("set".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("$3".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("aaa".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("$3".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
buf.writeBytes("bbb".getBytes());
buf.writeBytes(LINE);
ctx.writeAndFlush(buf);
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
System.out.println(buf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset()));
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 6379).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
|
http协议举例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
| package cn.itcast.advance.c2;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultFullHttpResponse;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpRequest;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus;
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpServerCodec;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LogLevel;
import io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_LENGTH;
@Slf4j
public class TestHttp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpRequest>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpRequest msg) throws Exception {
log.debug(msg.uri());
DefaultFullHttpResponse response =
new DefaultFullHttpResponse(msg.protocolVersion(), HttpResponseStatus.OK);
byte[] bytes = "<h1>Hello, world!</h1>".getBytes();
response.headers().setInt(CONTENT_LENGTH, bytes.length);
response.content().writeBytes(bytes);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
});
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
|
流程总结:
- 实例化ServerBootstrap
- 添加channel,添加group(处理的线程池)
- 添加childHandler:ChannelInitalizer
- pipeline中添加LoggingHandler
- pipeline中添加HttpServerCodec(http协议的编解码器)
- pipeline中添加SimpleChannelInboundHandler接受http请求,响应数据
- 绑定端口
- sync方法同步执行完
- 通过try catch finally关闭boss组和worker组。
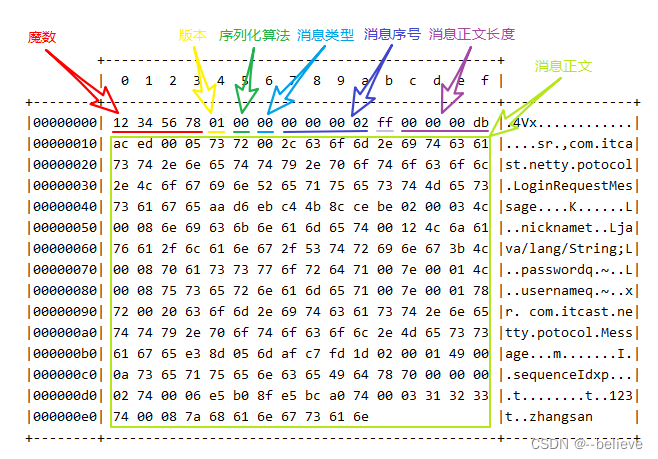
自定义协议要素
如果我们自定义一个协议需要哪些信息呢?
- 魔数:用来在第一时间判定是否是无效数据包,比如java字节码开头是CAFEBABE
- 版本号:标识协议的版本号,支持协议升级
- 序列化算法:消息正文到底采用哪种序列化反序列化方式。例如:Json,jdk等
- 指令类型:跟业务相关,是登录,注册,单聊,群聊等
- 请求序号:为了双工通信,提供异步能力
- 正文长度
- 消息正文
编解码器
根据上面的要素,设计一个登录请求消息和登录响应消息。使用netty完成收发
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| @Slf4j
public class MessageCodec extends ByteToMessageCodec<Message> {
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
out.writeBytes(new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4});
out.writeByte(1);
out.writeByte(0);
out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
out.writeByte(0xff);
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(msg);
byte[] bytes = bos.toByteArray();
out.writeInt(bytes.length);
out.writeBytes(bytes);
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
int magicNum = in.readInt();
byte version = in.readByte();
byte serializerType = in.readByte();
byte messageType = in.readByte();
int sequenceId = in.readInt();
in.readByte();
int length = in.readInt();
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
Message message = (Message) ois.readObject();
log.debug("{}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}", magicNum, version, serializerType, messageType, sequenceId, length);
log.debug("{}", message);
out.add(message);
}
}
|
测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(
new LoggingHandler(),
new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(
1024, 12, 4, 0, 0),
new MessageCodec()
);
LoginRequestMessage message = new LoginRequestMessage("zhangsan", "123", "张三");
ByteBuf buf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
new MessageCodec().encode(null, message, buf);
ByteBuf s1 = buf.slice(0, 100);
ByteBuf s2 = buf.slice(100, buf.readableBytes() - 100);
s1.retain();
channel.writeInbound(s1);
channel.writeInbound(s2);
|
解读
注意
- 在解码decode的时候,避免传过来的数据是不完整的,需要在codec前面加一个LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder验证数据的完整性(长度偏移,长度等)
- 在测试decode的时候,对数据进行分片了,要注意加上s1.retain(); // 引用计数 2。不然会引用数变为0ByteBuf被清理掉。出现IllegalReferenceCountException错误。
@Sharable
- 当handler不保存状态的时候,就可以安全的在多线程下共享。(加了这个表明handler是线程安全的)
- 但要注意对于编解码器类,不能继承 ByteToMessageCodec 或 CombinedChannelDuplexHandler 父类,他们的构造方法对 @Sharable 有限制,即明确了不能加@Sharable。换为继承自MessageToMessageCodeC父类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| @Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class MessageCodecSharable extends MessageToMessageCodec<ByteBuf, Message> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, List<Object> outList) throws Exception {
ByteBuf out = ctx.alloc().buffer();
out.writeBytes(new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4});
out.writeByte(1);
out.writeByte(0);
out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
out.writeByte(0xff);
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(msg);
byte[] bytes = bos.toByteArray();
out.writeInt(bytes.length);
out.writeBytes(bytes);
outList.add(out);
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
int magicNum = in.readInt();
byte version = in.readByte();
byte serializerType = in.readByte();
byte messageType = in.readByte();
int sequenceId = in.readInt();
in.readByte();
int length = in.readInt();
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
Message message = (Message) ois.readObject();
log.debug("{}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}", magicNum, version, serializerType, messageType, sequenceId, length);
log.debug("{}", message);
out.add(message);
}
}
|